How to Test Cors with Postman
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a common and crucial challenge. Especially in projects with a separation between front-end and back-end, developers often face the task of handling cross-origin requests.
In modern web development, Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a common and crucial challenge. Especially in projects with a separation between front-end and back-end, developers often face the task of handling cross-origin requests. Postman, as a powerful API testing tool, offers a convenient way to simulate and test CORS requests.
Use Cases
Using Postman to test CORS is highly meaningful in the following scenarios:
- Front-End and Back-End Separation: In projects where the front-end and back-end are separated, Postman helps developers simulate and test cross-origin requests, ensuring the smooth functioning of the system.
- API Development and Testing: Postman's intuitive interface and rich features make testing cross-origin requests easy during API development and testing.
- Debugging and Issue Resolution: When facing cross-origin issues, using Postman helps quickly pinpoint the problem, improving the efficiency of issue resolution.
Implementation Steps
Step 1: Create a New Request
In Postman, create a new request. Fill in the request's name and description, select the request type (GET, POST, etc.), and provide the request URL.
Step 2: Configure Request Headers
In the request settings, locate the "Headers" section. Add a new header with the key "Origin" and the value as your front-end domain. This simulates the Origin header sent by the browser during a cross-origin request.
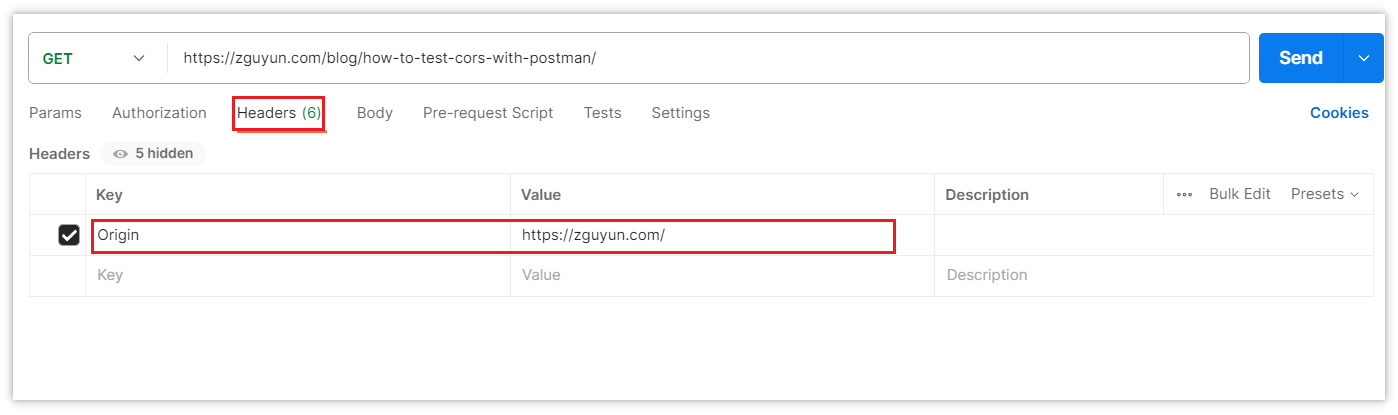
Step 3: Send the Request and View Results
Click the "Send" button in the Postman interface to send the request and view the results. Postman's user-friendly interface allows you to see all details of the request and response, facilitating debugging and analysis.
Step 4: Check CORS Response Headers
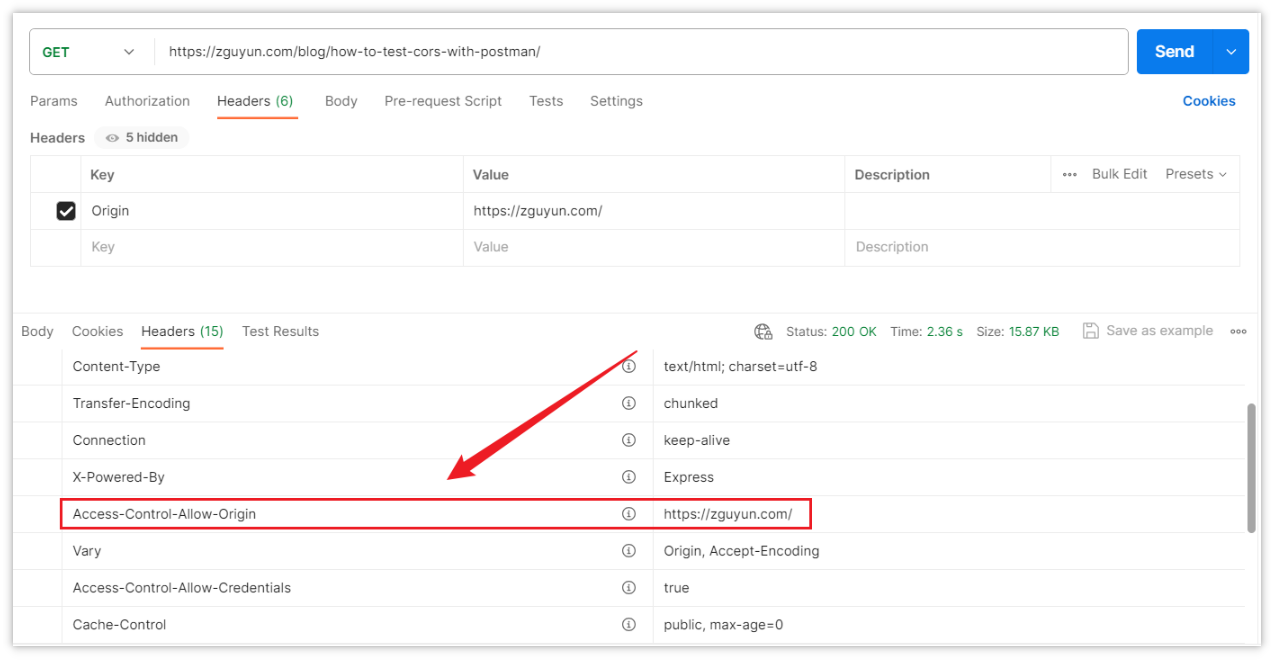
Inspect the response headers for CORS-related information, such as "Access-Control-Allow-Origin." Ensure that the back-end server is correctly configured with CORS to allow requests from the front-end domain.
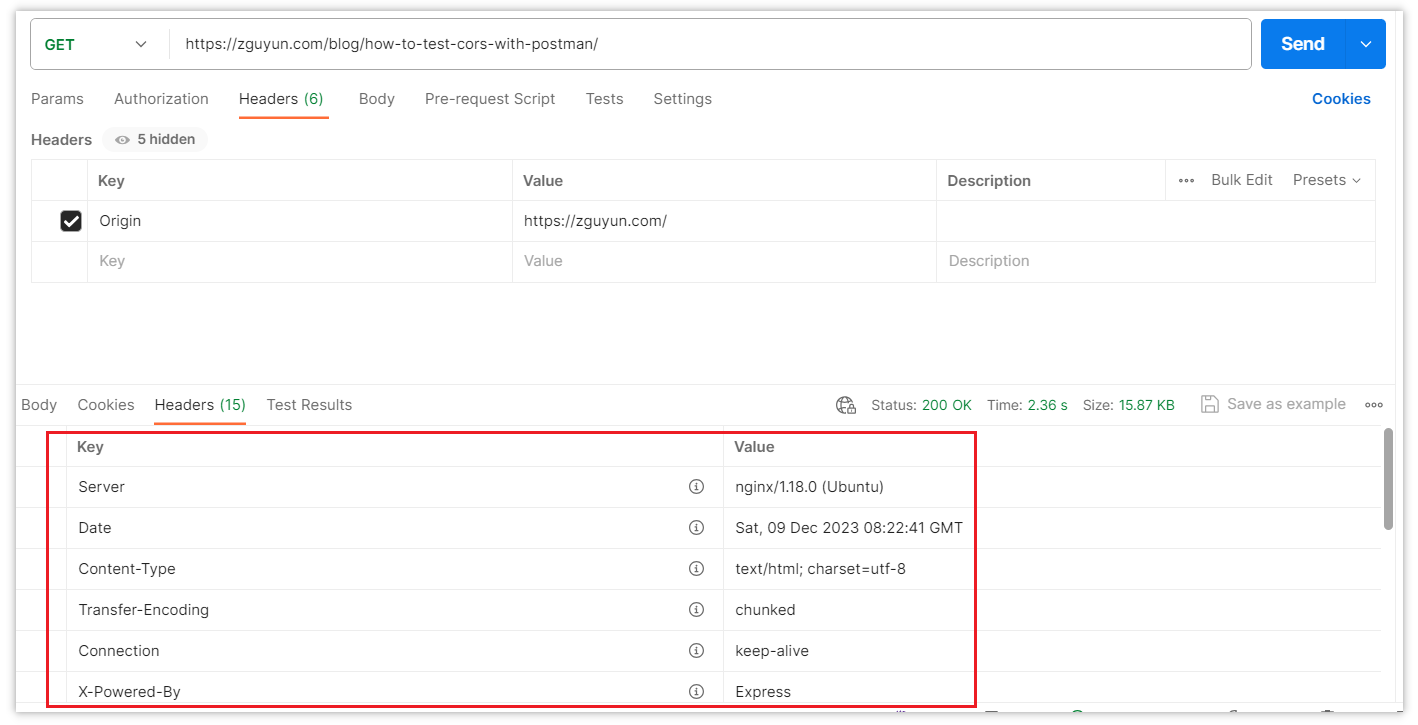
Whether the cross-origin request is successful or not, the returned status code is 200. To confirm whether the cross-origin was successful, it is necessary to check the response headers.
In case of unsuccessful cross-origin requests, the response will not include headers related to cross-origin:
For successful cross-origin requests, the response will include headers related to cross-origin:
Tips, Tricks, and Considerations
- Use Environment Variables: If frequently testing cross-origin requests in different environments, leverage Postman's environment variable feature to easily switch between configurations.
- Review Console Logs: Check the console logs in the browser's developer tools for additional information on cross-origin requests, aiding in issue resolution.
Conclusion
Through this guide, we've learned how to use Postman to test Cross-Origin Resource Sharing. From creating a request to configuring headers and sending requests, to checking CORS response headers, these steps assist developers in better understanding and addressing cross-origin request challenges. Postman provides a robust and flexible toolset, making testing cross-origin requests an efficient process.
References
Learn more:
- How to Send JSON Data in Postman
- NextJS vs RedwoodJS
- How to configure hosts in Postman?
- Comprehensive Guide to Implementing Automated Testing in Postman: A Deep Dive
Article Link:https://zguyun.com/blog/how-to-test-cors-with-postman/
ZGY:Share more interesting programming and AI knowledge.