How to Set Up a Bearer Token in Postman?
This article elaborately explained how to set up Bearer Tokens in Postman. Correctly setting up Bearer Tokens is a crucial step in accessing protected APIs, and Postman provides a convenient interface to perform this operation.
In modern software development, Web APIs play a crucial role, enabling data exchange and communication between different systems. However, many APIs require client authentication to protect sensitive data and resources. Among these, Bearer Token is a common authentication token that allows clients to access protected API resources. This article will explain how to set up a Bearer Token in Postman for accessing protected APIs.
1.Preparation
Before proceeding, the following preparations are necessary:
- Download and install the Postman application, ensuring it is the latest version.
- If not already registered, sign up and log in to your Postman account.
- Prepare a protected API that you need to access and ensure you have obtained the corresponding access token.
2.Setting up Bearer Token in Postman
2.1 Create a Request in Postman
Launch the Postman application and ensure you are logged into your account. Click the "New" button at the top left corner of the interface to create a new request.
2.2 Add Authorization Header
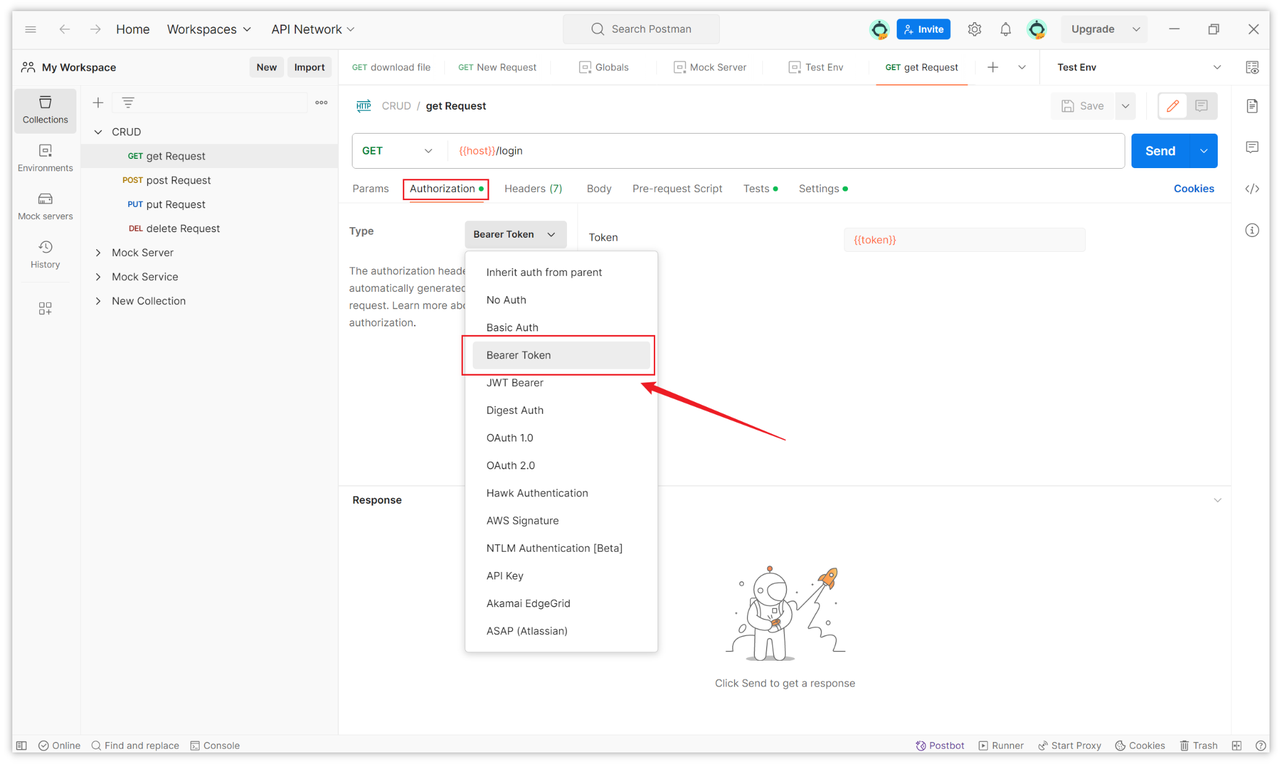
In the Headers section of the request, locate the "Authorization" header and click on the dropdown menu on the right side. Select "Bearer Token" as the authorization type.
2.3 Enter Bearer Token
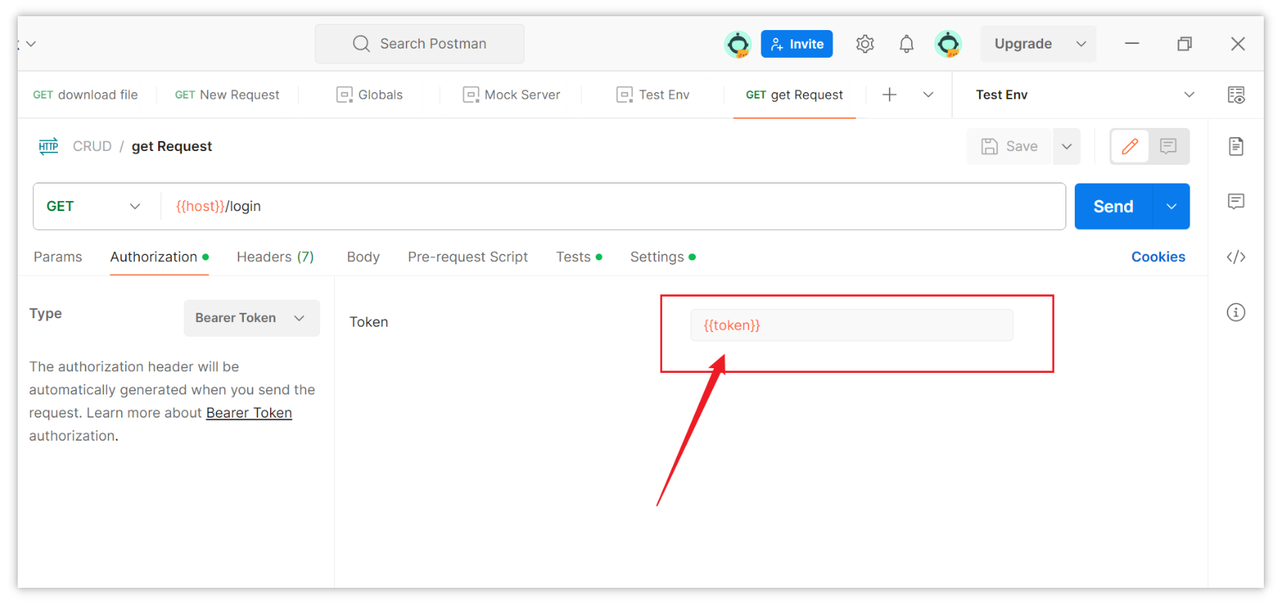
In the "Bearer Token" field, enter your Bearer Token, ensuring accuracy. You can store the token credentials returned by the backend in environment variables and then reference them using {{}} syntax.
For example, if the backend returns the following JSON data structure:
{
"code": "0",
"message": "success",
"data": {
"accessToken": "wueigh982gu09fdiogh98ut934w0u24u98ugwr0w942hbj0wposdjvb09g3rugj029wrobnv-wpekdvd093yu8340w9-ig9h294-2gho2jwe0gjr90gjwrpvogiojdfg",
"userId": "10f8h983hg9uhrsoigidigos"
}
}You can write a script in Postman's Tests to extract the accessToken value into an environment variable and then assign it in the Authorization by referencing the variable. A script example is as follows:
var body = pm.response.json();
var token = body.data.accessToken;
console.log("token:" + token);
pm.environment.set("token", token);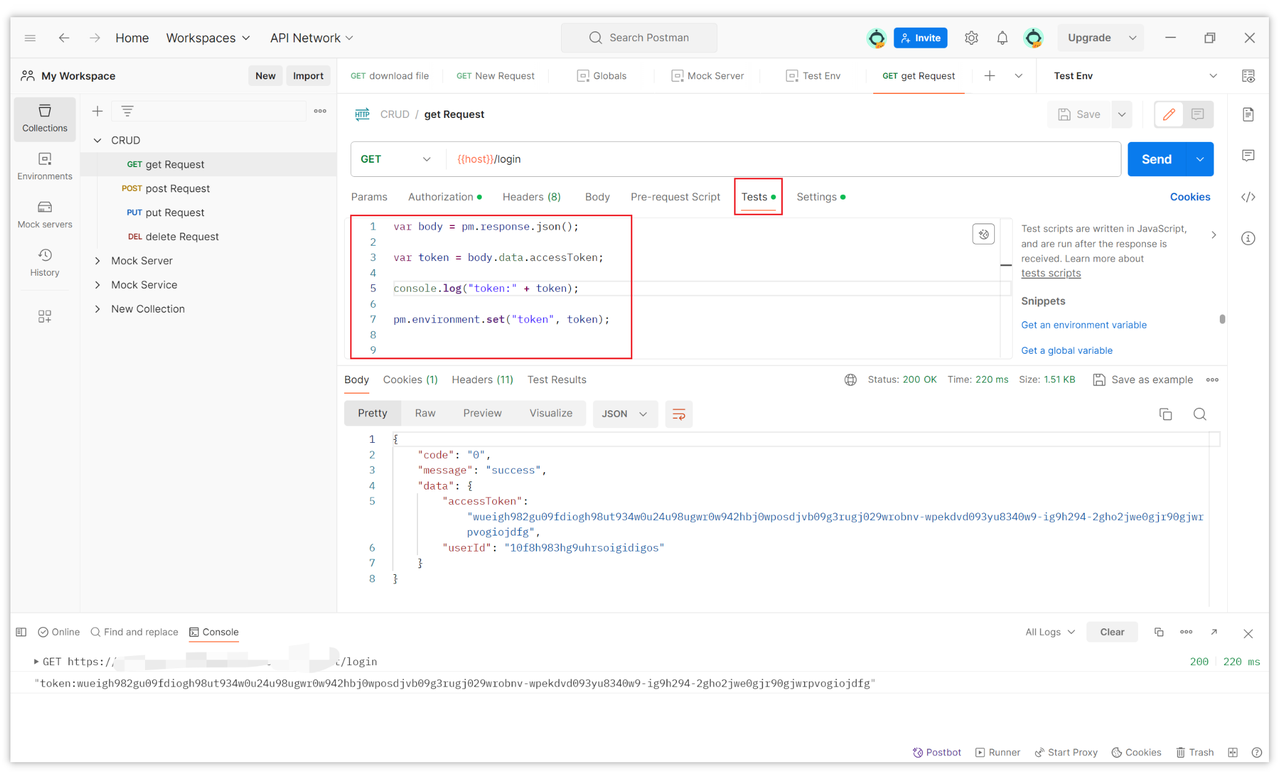
Extracted token in environment variable:
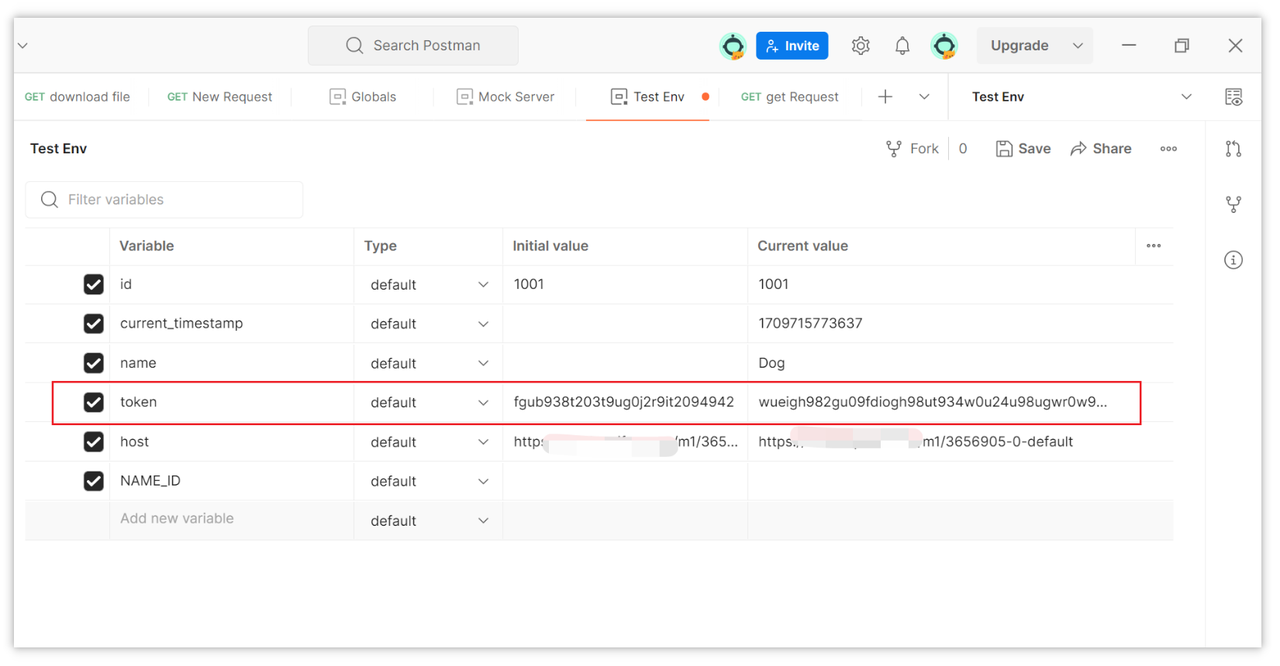
Normally, tokens are configured in the collection instead of individual endpoints. This way, all endpoints under this collection will automatically carry the configured token credentials when making requests.
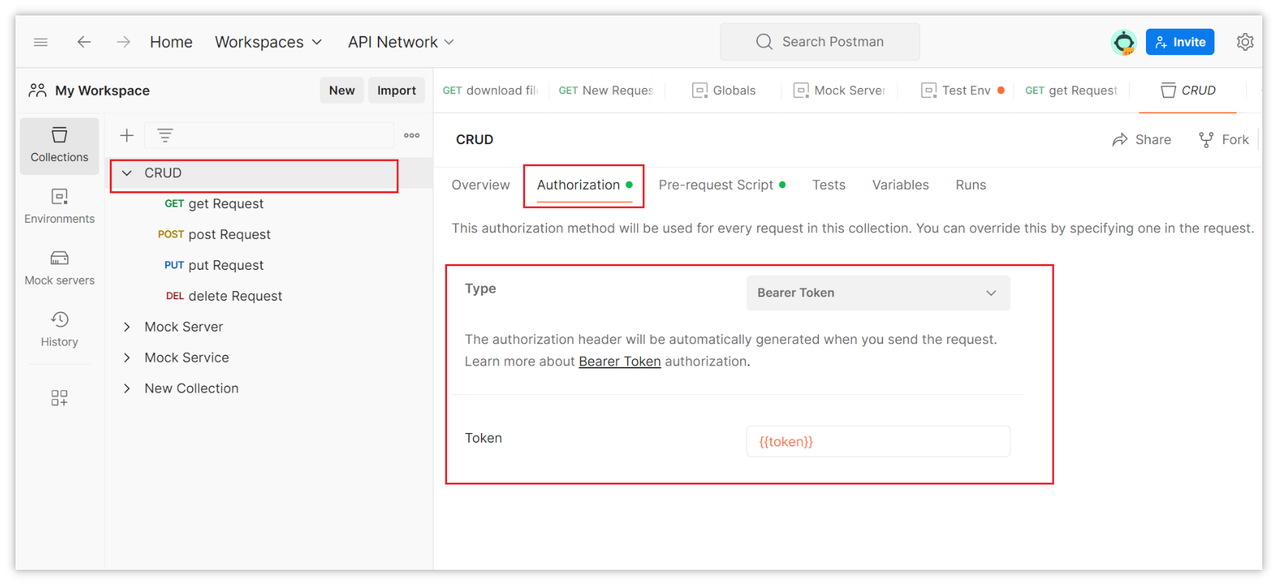
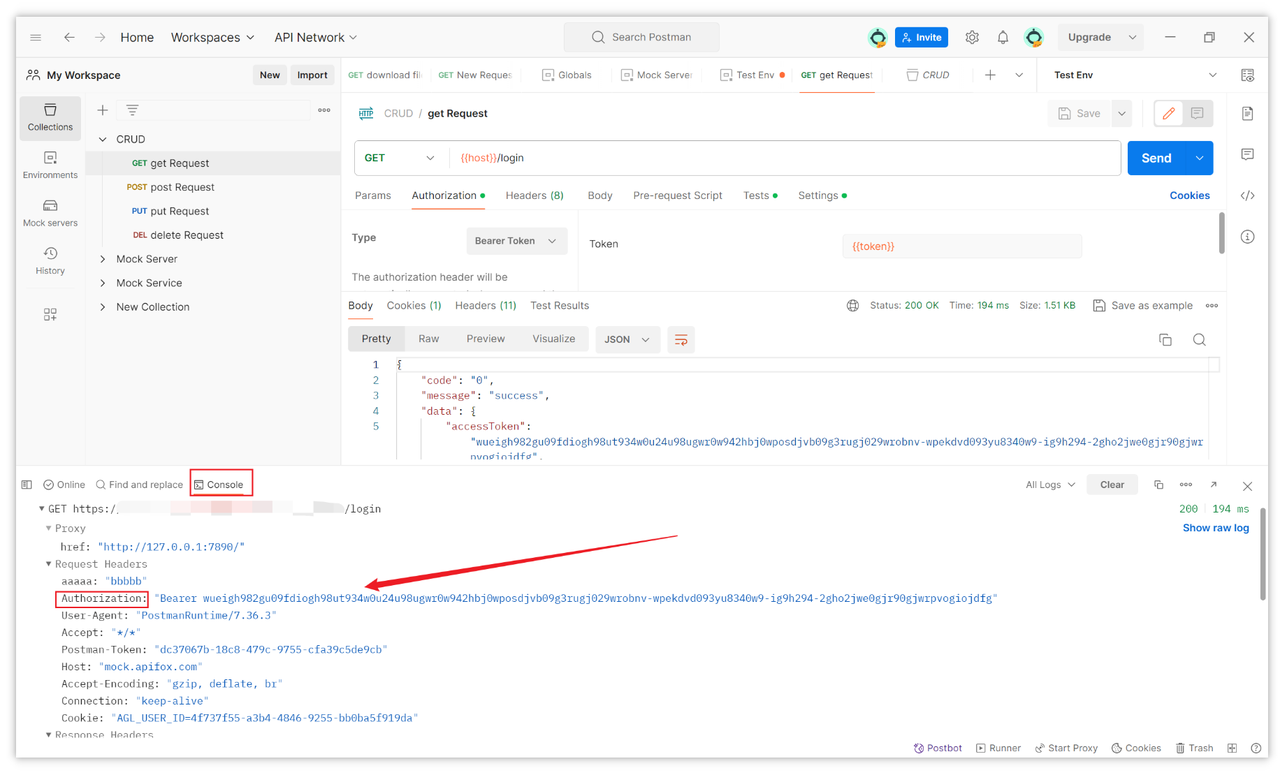
3.Send the Request
Once the Bearer Token is correctly set, you can add any other request parameters (if any) and then click the "Send" button at the top right corner of the interface to execute your request. After successful sending, you can check if the Bearer Token is included in the console below.
4.Considerations and Recommendations
When using Bearer Token for API access, consider the following:
- Security: Ensure not to leak Bearer Tokens to unauthorized individuals.
- Token Management: Properly manage and store your access tokens to ensure security.
- Error Handling: Handle potential authentication errors or token expiration.
Conclusion
This article elaborately explained how to set up Bearer Tokens in Postman. Correctly setting up Bearer Tokens is a crucial step in accessing protected APIs, and Postman provides a convenient interface to perform this operation. You can try and implement the knowledge above to effectively utilize Postman and Bearer Tokens for API access in your daily development tasks.

Learn more:
- How to open and use the Console in Postman?
- How to Import and Export Environment Variables in Postman?
Learn more:
